Scar correction
 Scar formation is a very important process thanks to which our body repairs the damage it suffered. It is a process that all of us have sooner or later experimented on our skin. It occurs repeatedly. Many are the variants that may contribute to determine its final outcome. Much depends on the starting-lesion, on the damaging agent and on the characteristics of the involved tissue. The site of trauma is of large importance as well. There are parts of the body that scar better, while others heal leaving more evident signs behind. The reconstructive plastic surgeon is certainly the specialist with wider experience in this field. He/she is therefore the most qualified to give advice on the opportunity of correcting any residual scarring. Scars are permanent marks. They may improve with time but will never disappear. Any surgical procedure aimed at improving the scar, will not perfectly erase the scar, but only make it less evident. In other words an ugly and visible scar will be substituted with a much more acceptable one. Your surgeon will certainly clearly explain to you that any scar's appearance can be improved so as to make it less visible, less evident and more easily covered by make-up.
Scar formation is a very important process thanks to which our body repairs the damage it suffered. It is a process that all of us have sooner or later experimented on our skin. It occurs repeatedly. Many are the variants that may contribute to determine its final outcome. Much depends on the starting-lesion, on the damaging agent and on the characteristics of the involved tissue. The site of trauma is of large importance as well. There are parts of the body that scar better, while others heal leaving more evident signs behind. The reconstructive plastic surgeon is certainly the specialist with wider experience in this field. He/she is therefore the most qualified to give advice on the opportunity of correcting any residual scarring. Scars are permanent marks. They may improve with time but will never disappear. Any surgical procedure aimed at improving the scar, will not perfectly erase the scar, but only make it less evident. In other words an ugly and visible scar will be substituted with a much more acceptable one. Your surgeon will certainly clearly explain to you that any scar's appearance can be improved so as to make it less visible, less evident and more easily covered by make-up.
 |
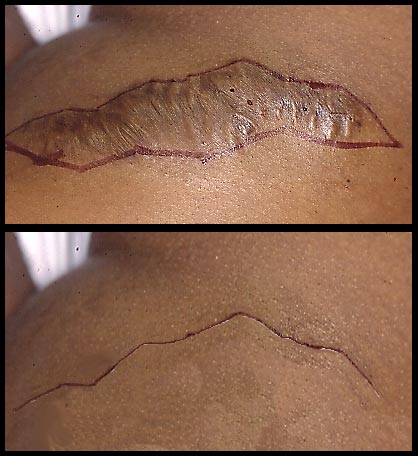
| Multiple Z-scars: example of cicatricial bridle corrected by means of multiple Z. |
The success of a corrective operation depends on many factors: the size of the scar, its shape, the anatomical region it occupies, the age of the patient, hereditary factors and skin general conditions. The scar can be normal or pathological, such as in the case of hypertrophy or in the less frequent one of distrophic scars or keloids. Hypertrophic scars are often erroneously defined as keloids.
Hypertrophic Scars
What characterizes this kind of scar is the excess of fibrous tissue during the wound's healing period. The scar itself appears red and the tissue becomes harder and more prominent than the surrounding skin.
 |
| The cheloid scar |
The keloid scar
This kind of scar has more or less the same characteristics of the hypertrophic one but has the tendency to expand to the healthy tissues. These are very exuberant scars that will remain bright red and a very thick . The areas where keloids are more likely to occur are ear lobes, neck and chin.
Acne Scars
Acne scars are quite common on both face and shoulders. They show in shape of little craters with a limited glossy surface. The scar appears more pigmented than the normal cutis.
Each kind of scar calls for a meticulous study to decide what operation will allow getting the best results with minimal risks. The most frequent treatments are:
- Excision
In spite of the fact that scars can never be completely eliminated, cicatricial tissue can be removed and the edges sutured as to create a thinner scar. Wide scars or those located in areas under tension can be removed resecting them step by step rather than all at once, excising one small portion of scar each time thus allowing a correct readjustment of the surrounding cutis. The term excision also includes those surgical procedures by means of which the plastic surgeon repositions and adjusts the scar in order to make it less visible. The surgeon will try to reposition the scar only when it could be hidden within the skin's natural lines. Should this not be possible, the scar could be reshaped by dividing it into little segments that will more easily be camouflaged by the skin tissue (Multiple Z technique). - Collagen injections
Injectable collagen is a natural product of bovine origin; its main quality is to blend perfectly with the subcutaneous tissue. It is reabsorbable though and necessitates periodical re-infiltration. It is used for rather shallow grooves. - Steroid injections
Keloids and hypertrophic scars improve with the steroid injection. This kind of procedure has the purpose of stabilizing the scarring process and avoid any further fibrous tissue deposition. Furthermore, the scars tend to take on a more natural color, thanks to the anti-inflammatory action of the drug. - Dermoabrasion
Some scars can be abraded. The technique is called dermoabrasion and consists in employing a rotating bur that smoothens the skin, making it more even. Dermoabrasion is often associated to other surgical procedures with the main purpose of attenuating skin aging signs.
How to make up your mind on the operation to choose
Most scars improve with time, therefore, before deciding to resort to surgery one should wait for the healing process to be completed. Normally this takes a few months but it might be advisable to wait over one year before any surgical treatment.
Anche nel caso della correzione di cicatrici da acne si deve aspettare che la cute si sia stabilizzata. Chiunque sia interessato ad un intervento di revisione di una cicatrice deve consultare un Chirurgo Plastico competente. Durante la visita iniziale il Chirurgo valuterà le caratteristiche della cicatrice per determinare quale tipo di chirurgia sia la più indicata. A questo punto, descritti i rischi e i benefici, sarà il paziente a decidere se sottoporsi o meno all'intervento. Oltre all'abilità del chirurgo, ci sono altre considerazioni importanti prima di prendere una decisione : -le aspettative del paziente e le motivazioni che lo spingono a sottoporsi a una correzione . Verranno eseguite delle fotografie pre e post-operatorie. Queste fotografie faranno parte dell'archivio del Chirurgo e potranno essere confrontate a quelle che si faranno qualche tempo dopo l'operazione.
Dove viene eseguito l'intervento
Nella maggior parte dei casi gli interventi di revisione delle cicatrici vengono eseguite in regime di day-hospital ed in anestesia locale. Una correzione cicatriziale più estesa a volte può richiedere una anestesia generale e necessitare di un ricovero in una Clinica specializzata.
L' immediato post-operatorio
La maggiore parte dei pazienti sottoposti a revisione di cicatrice non accusano dolore o disagi. La parte operata viene medicata con cerotti e garze protettive che verranno cambiate nei giorni successivi . Nel caso in cui si esegua una dermoabrasione, la parte tratta verrà coperta con una medicazione non adesiva associata ad un bendaggio occlusivo.
Le aspettative
Le cicatrici non possono essere totalmente rimosse, come già sottolineato, ma possono essere solo migliorate nel tempo. Se ci si aspetta di vedere scomparire come per magia la cicatrice è meglio rinunciare all'intervento . Siccome dopo l'intervento la cicatrice ripartirà da zero, per alcuni mesi risulterà rossa e quindi più evidente di prima dell'intervento .
I rischi
I rischi sono minimi, ed in genere corrispondono a quelli di un qualsiasi intervento chirurgico. Ogni anno vengono eseguiti numerosissimi interventi di revisione cicatrici e non sono descritte complicazioni importanti .
Il costo
Il costo varia a seconda dell'estensione e della complessità della cicatrice. Il chirurgo ed il suo "staff" presenteranno un preventivo prima dell'operazione. Generalmente un'assicurazione può coprire il costo dell'intervento di revisione di cicatrice, specialmente se questa é dovuta ad un incidente. La miglior cosa da fare é quella di consultare prima dell'intervento la propria compagnia assicuratrice
